Full-suspension mountain bikes can use single or quite a few pivot areas, utterly utterly totally different linkages and swingarm designs to assist dictate their suspension traits.
What number of pivots and hyperlinks are used and one of the best ways they’re laid out helps to learn the way the bike will work, one of the best ways it’ll really actually really feel on the path and how much driving it could be greatest suited to.
Correct proper right here we clarify the varied types of mountain bike rear suspension, the technical phrases used to elucidate suspension kinematics and one of the best ways bike producers alter or change their suspension designs to create specific suspension traits.
You possibly can skip to the utterly utterly totally different sections by hitting the hyperlinks beneath:
How do suspension designs impression a bike’s effectivity?
Though rear-suspension design can differ significantly from model to model, the job is regularly primarily the an similar: to soak up bumps and impacts as efficiently and effectively as doable.
In any case, it’s a bit additional superior, due to the suspension must accommodate the rider shifting about on prime of the bike, pedalling and braking whereas navigating the path beneath their tyres. Suspension designs ought to topic all of this stuff in.
Impact absorption

The primary job of a rear suspension system is to soak up have an effect on forces attributable to the rear wheel hitting a bump or impediment, which causes the suspension to compress.
A motorcycle’s means to soak up an have an effect on is principally influenced by quite a few elements:
- The axle path is the road the rear axle traces on account of the suspension cycles by way of its journey. Axle paths could be ahead, vertical, reward or S-shaped. Its path is dictated by the place of the physique’s pivot elements.
- Pivot areas dictate the axle’s path at a given diploma contained in the journey.
- Leverage ratio/curve is the connection between how tons the rear wheel strikes and one of the best ways tons the shock compresses on account of the suspension cycles. For instance, if a bike’s frequent leverage ratio is 3:1, when the rear axle strikes 30mm, the shock will compress by 10mm.
The leverage ratio can change all by way of the bike’s journey (producers will plot this on a leverage curve graph as an example how this adjustments). That is arguably additional important than the frequent leverage ratio.
Beginning with a excessive leverage ratio means the shock could be compressed additional merely, providing additional preliminary sensitivity and probably additional grip. Inside the path of the very best of the journey, a decrease leverage ratio helps to up the quantity of vitality required to compress the shock, rising the extent of progress and making it tougher to backside out (use the entire suspension journey) - Shock absorber and spring. With out these, the suspension system can’t soak up impacts. Springs present the resistance to soak up the compression forces from an have an effect on and rebound or return the suspension system to its real, uncompressed (or sagged) place.
Practically all rear shocks will attribute some kind of in-built damping. This controls the tempo at which the shock compresses and rebounds, normally by pushing oil by way of a gaggle of ports and shims to create resistance. With none kind of damping, the spring would oscillate uncontrollably.
Widespread suspension designs outlined
Now we perceive what a mountain bike suspension system is meant to do, and the numerous elements that affect one of the best ways it performs, let’s have a look on the principle suspension designs throughout the market.
We’ll furthermore define the professionals and cons of every.
Single pivot

The one pivot is the right suspension design in use correct this second.
Correct proper right here, the rear axle is alleged to the principle physique by a swingarm, with no extra pivots in between. The axle strikes in a seamless arc, centred on the one pivot diploma.
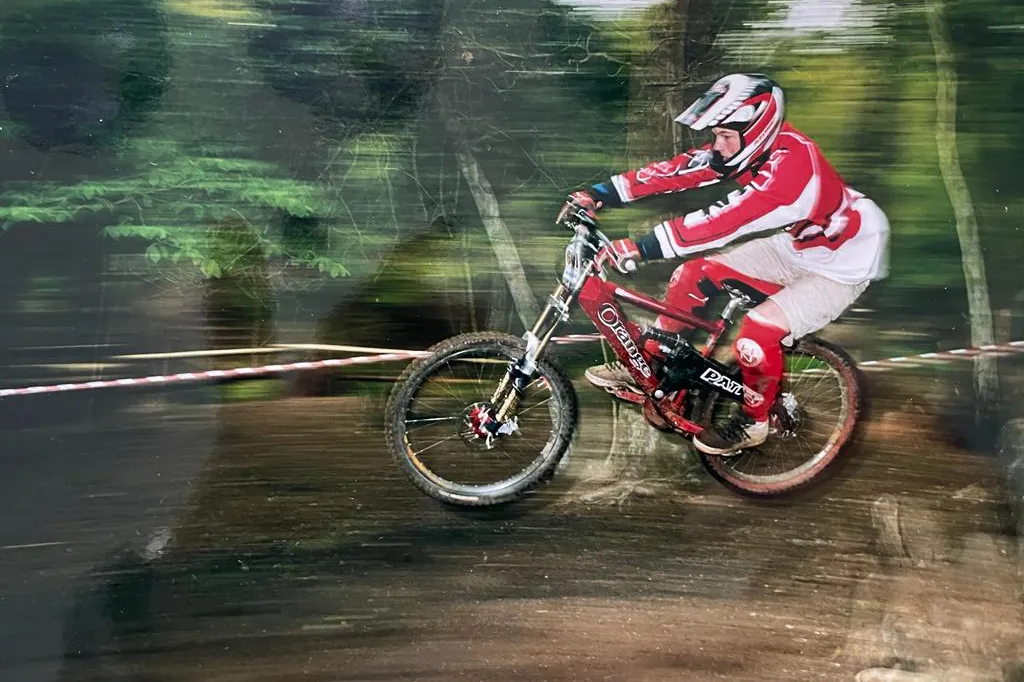

Contained in the case of an precise single pivot, the shock is alleged on to the swingarm – a design made well-known by Orange Bikes.
One doable shortcoming of this design is that it affords little administration over the leverage curve.
True single-pivot bikes are sometimes fairly linear. The power required to maneuver the rear wheel by way of its journey doesn’t ‘ramp up’ throughout the path of the very best of the physique’s journey to withstand bottom-out, as it may well with an extra progressive design.
Professionals
- Easy
- Requires fewer bearings and makes for simpler repairs
- The suspension motion is fastened by way of its journey
Cons
- Offers little administration over the leverage curve
- May be too linear for coil shocks
Linkage-driven single pivot
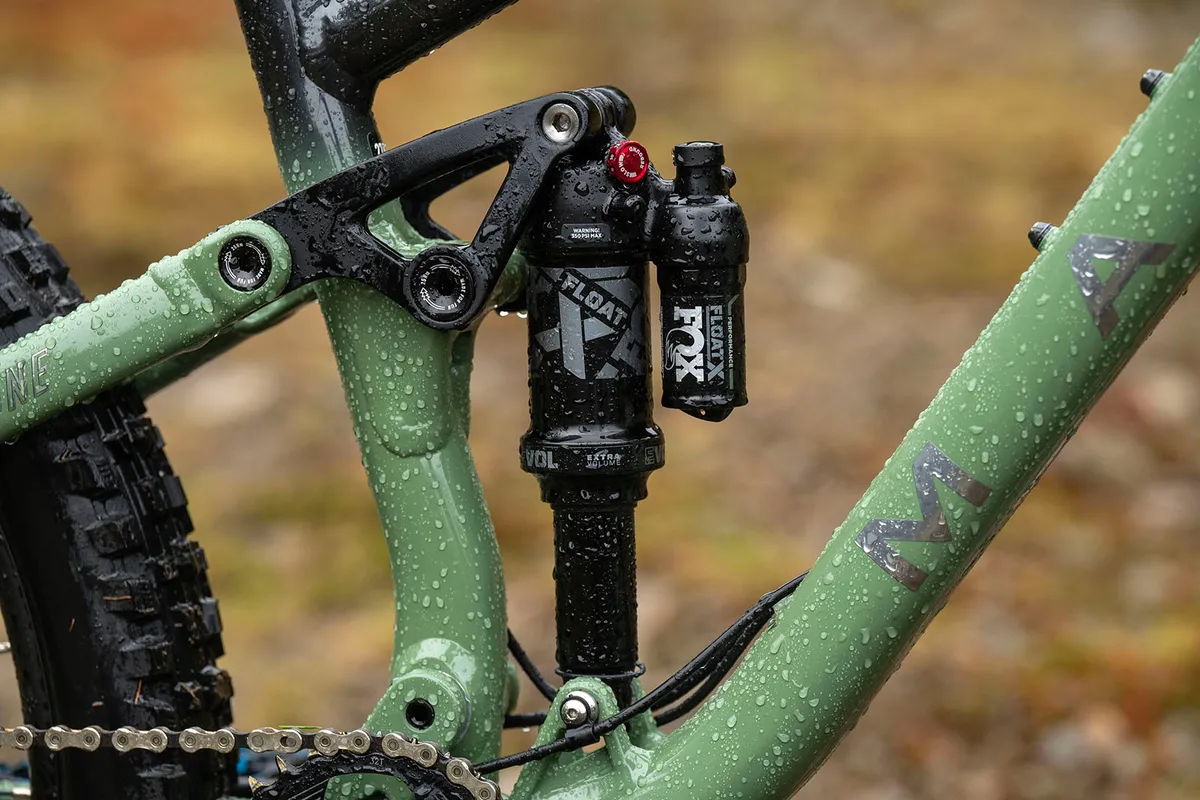

A linkage-driven single-pivot design, as seen on the Marin Rift Zone, nonetheless makes use of an uninterrupted swingarm, connecting the rear axle on to the mainframe.
Nonetheless, it incorporates some kind of linkage to drive the shock. This permits the physique designers to manage the leverage curve and administration the physique’s progressivity.
The design seems to be very like a four-bar (Horst-link) design, so is also known as ‘faux-bar’. Nonetheless the rear axle continues to be straight related to the principle pivot via the chainstay, in order that’s merely one totally different kind of linkage-driven single pivot.
Professionals
- Further leverage curve tunability than an precise single-pivot MTB
Cons
- Elevated repairs over single pivot
- Mounted on the spot centre limits the tuning of some suspension traits
Trek ABP and DW split-pivot methods

This design is unquestionably a linkage-driven single pivot, along with that Trek makes use of a concentric dropout pivot on the rear axle. This permits Trek to mount the brake caliper to the seatstay comparatively than the chainstay.
Due to the seatstays rotate lots a lot much less all through the disc rotor than the chainstays on account of the suspension cycles, the have an effect on of anti-rise is considerably diminished.
In a number of phrases, Trek’s design works like a linkage-driven single pivot in relation to pedalling forces, nonetheless like a Horst-link in relation to braking forces. It’s one issue of a hybrid.
Professionals
- Considerably diminished anti-rise
Cons
- Elevated repairs over single pivot
Excessive pivot
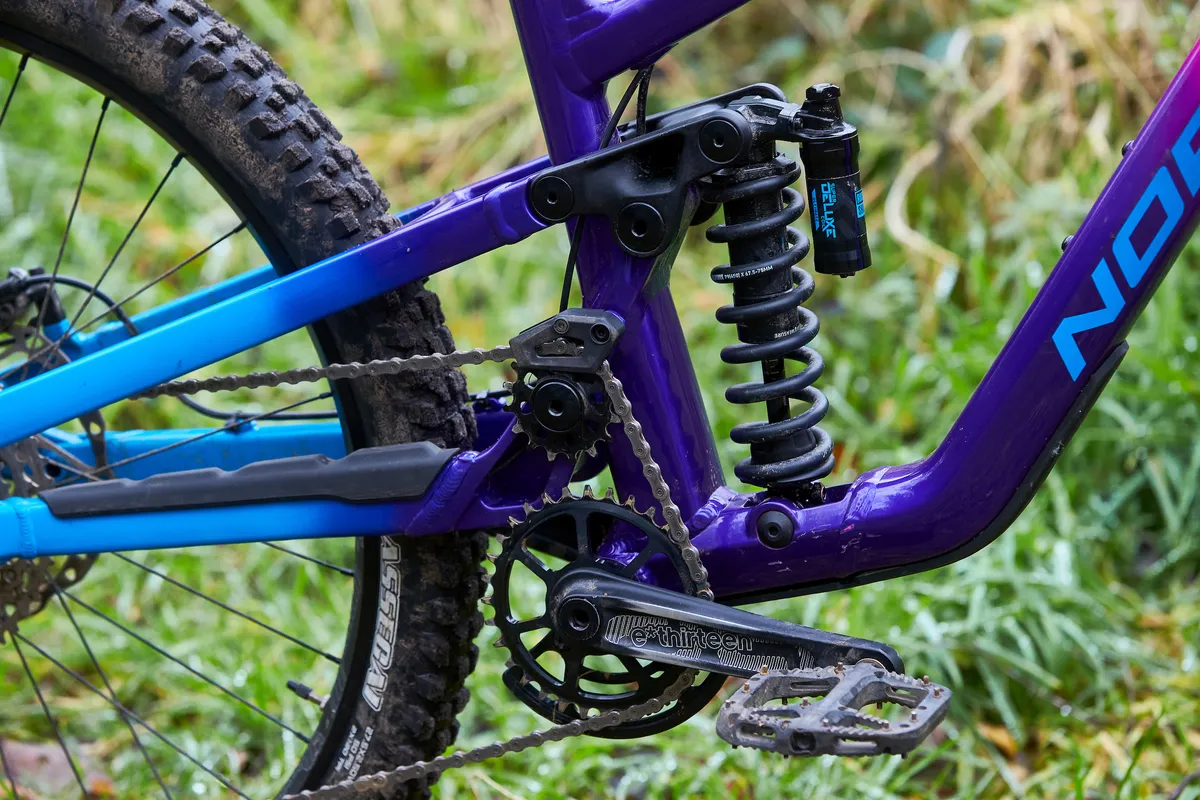

Excessive-pivot bikes have a pivot diploma positioned tons larger than frequent, nonetheless shifting the pivot larger alone would end in unacceptably excessive ranges of pedal kickback.
Utilizing an loafer pulley, which routes the chainline up earlier the pivot diploma, might help to mitigate pedal kickback and be used to tune anti-squat traits.
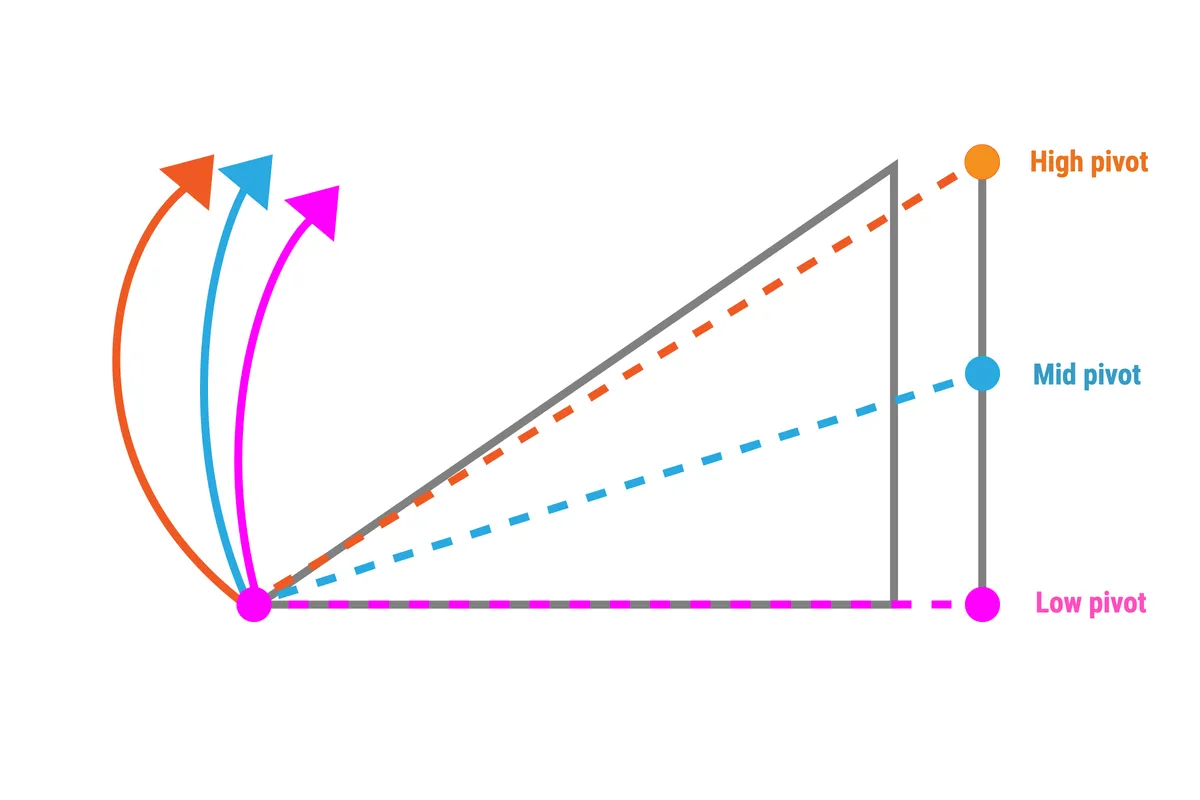
Some good benefits of this design are two-fold. First, it affords a rearward axle path. This in itself might help the rear wheel to cope with square-edge hits and contributes to the ultimate pedalling effectivity of the bike.
Second, due to the chain passes appropriate by the pivot diploma, there’s subsequent to no pedal kickback. This additional improves suspension sensitivity.
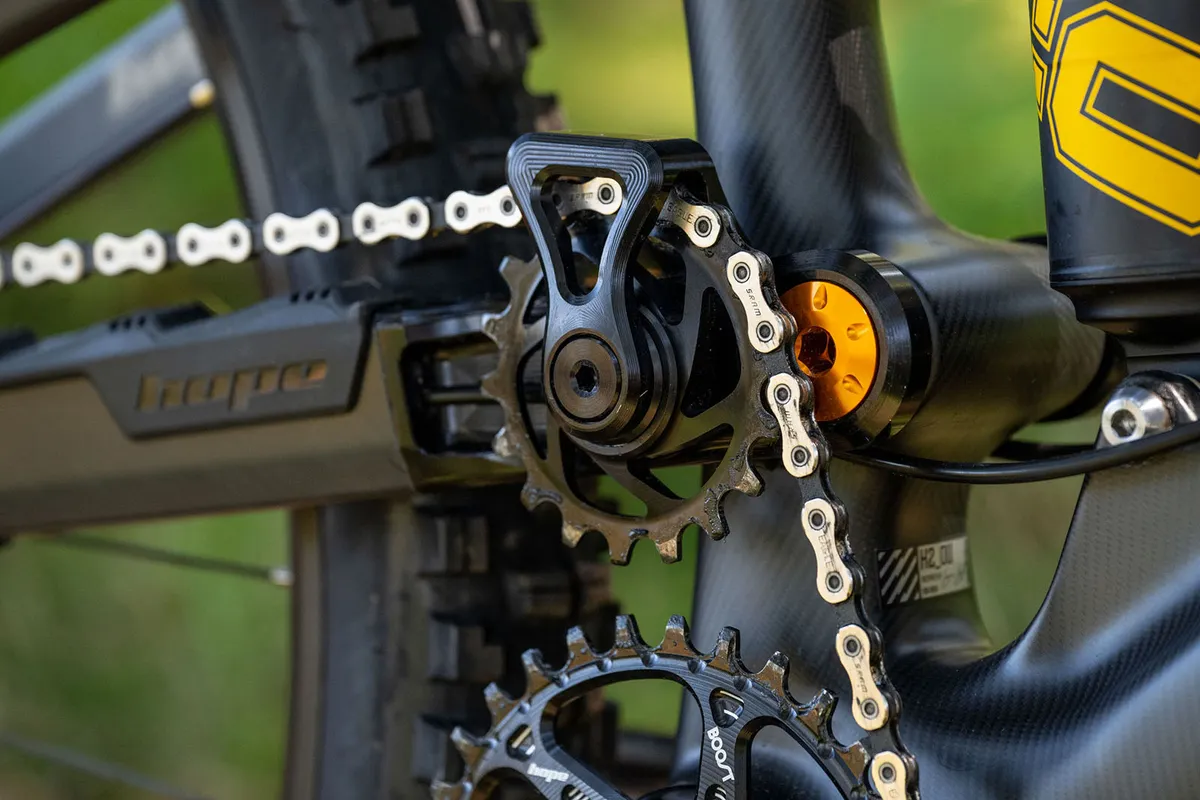

Potential disadvantages of high-pivot designs would possibly embrace elevated drivetrain drag and upkeep due to the loafer pulley, and a few designs might need excessive ranges of anti-rise because of the excessive pivot diploma.
Fully totally different designs want longer chains to accommodate the loafer’s location, perhaps along with value and weight. Plus the rear centre grows all by compression (by various parts, relying on the design used), perhaps creating uncommon dealing with traits.
Professionals
- The rearward axle path helps the bike protect momentum over square-edge impacts
- Very low ranges of pedal kickback
Cons
- Elevated repairs
- Potential for drivetrain drag
- Excessive ranges of anti-rise in some situations
- Rear centre will enhance in dimension, producing odd dealing with traits
- Some designs want longer chains than common suspension methods
Horst-link (four-bar)

Horst-link (moreover known as four-bar) suspension – utilized by Specialised, Norco and a great deal of additional – is marked out by a rear pivot situated beneath and in entrance of the rear axle on the chainstay.
This implies the rear axle is just not straight related to the mainframe, and so it strikes in a path outlined by its on the spot centre and centre of curvature.
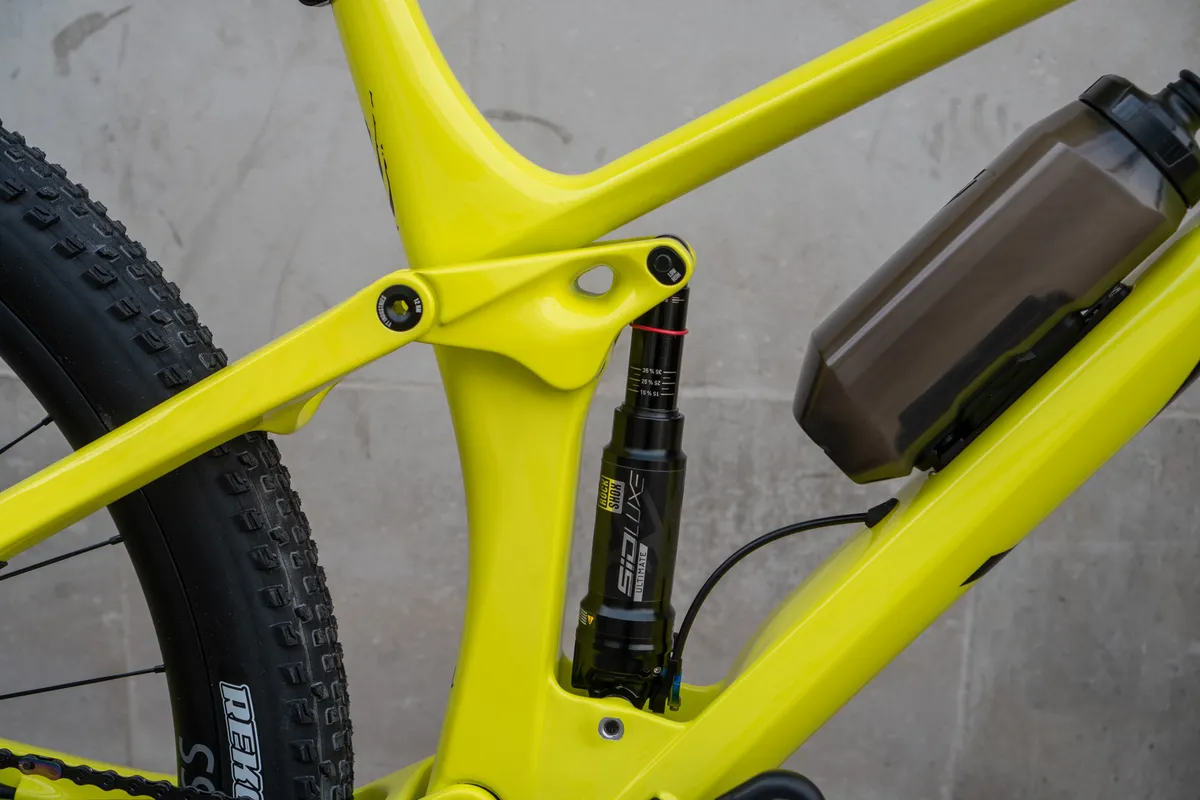

The second centre and centre of curvature would possibly change on account of the suspension cycles by way of its journey.
Relying on the design, the have an effect on of braking forces on the suspension (anti-rise) could be diminished and administration over the degrees of anti-squat could be elevated, relative to a single-pivot design.
A variation of the Horst-link could be discovered on the high-pivot Forbidden Druid, which flips the four-bar system the flawed methodology up.
Professionals
- Offers excessive ranges of tunability of all suspension traits and predictable suspension curves
Cons
- Further pivots to keep up in contrast with a single-pivot design
Twin-link (digital pivot)

Twin-link designs, moreover known as digital pivots, use a inflexible rear triangle, which articulates on a pair of non permanent hyperlinks connecting it to the mainframe.
It really works within the similar decision to a Horst-link design. Take into accounts shifting the Horst-link’s chainstay pivot tons nearer to the mainframe and you’ve got the premise of a twin-link system. The one exact distinction is the size of the decrease hyperlink.
As with the Horst-link design, the axle path of a twin-link system is tangential to a shifting on the spot centre, whereas centre of curvature, or ‘digital pivot diploma’, defines one of the best ways whereby by way of which the axle path curves by way of its journey.
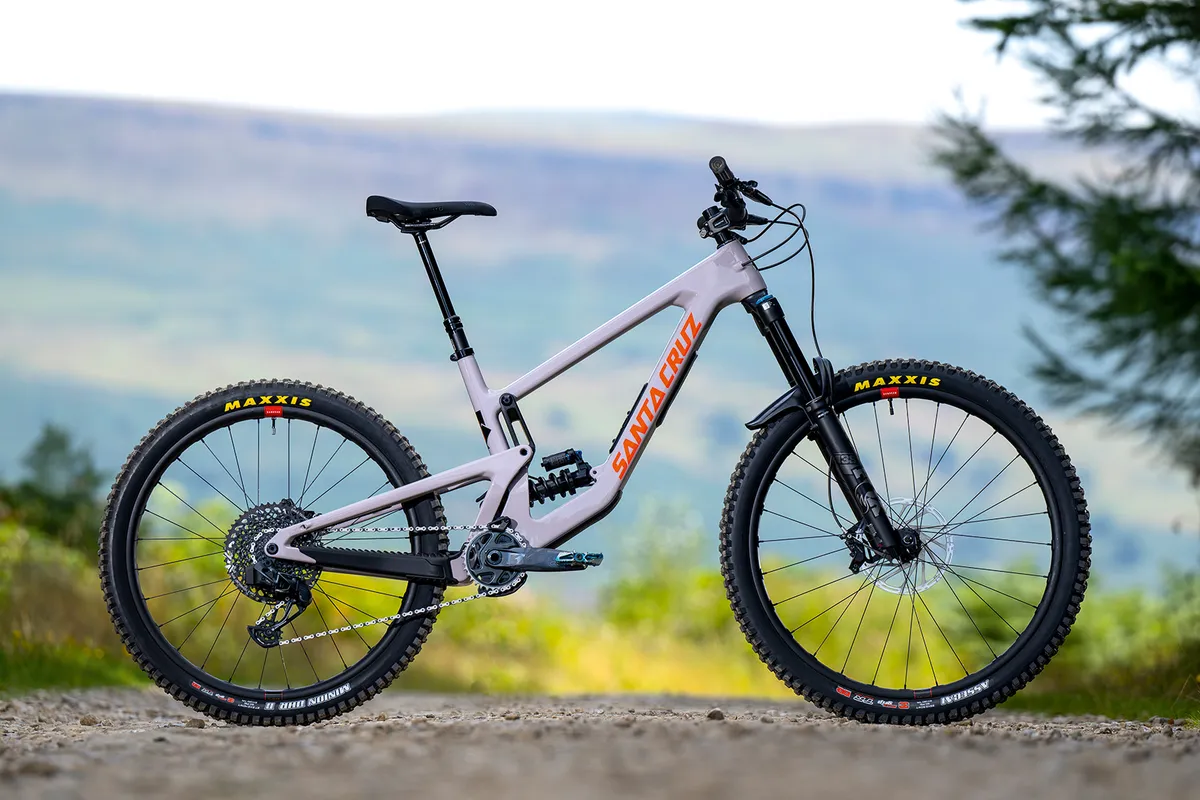

Some twin-link designs, resembling Santa Cruz’s VPP system, use hyperlinks that counter-rotate (flip in reverse instructions), whereas many others, resembling Large’s Maestro system, have hyperlinks that co-rotate (flip throughout the an similar path).
The simplest method the centre of curvature migrates on account of the bike strikes by way of its journey is type of utterly utterly totally different for every configuration.
The fact is, twin-link or Horst-link bikes with co-rotating hyperlinks normally exhibit anti-squat behaviour that’s identical to a single-pivot bike.
Counter-rotating hyperlinks can produce an anti-squat profile that peaks within the midst of the journey, which could be fascinating in relation to balancing pedal effectivity in opposition to pedal kickback.
This distinction between counter-rotating and co-rotating hyperlinks is additional important in relation to suspension kinematics than the arbitrary distinction between Horst-link and twin-link designs.
Professionals
- Offers excessive ranges of tunability of all suspension traits and predicable suspension curves
Cons
- Elevated repairs and prices over single pivot
Six-bar suspension designs

Till not too long ago multi-link six-bar suspension designs have been comparatively unusual, nonetheless bikes resembling Felt’s Equilink current the design has been used for fairly a while.
Producers resembling Atherton Bikes, Commencal and Yeti have been behind a resurgence of the six-bar design, placing it as soon as extra contained in the limelight.

In some examples, such on account of the Canyon Sender, and Specialised’s Enduro and Kenevo SL, the bike’s on the spot centre is printed by the principle four-bar system. The shock is pushed from a separate linkage system, taking the ultimate variety of hyperlinks to 6.
Attempting intently on the linkage design seen on Atherton Bikes and Commencal, the additional two hyperlinks are in between the chainstay and the principle physique.
Professionals
- Offers excessive ranges of tunability of all suspension traits and predictable leverage curves
Cons
- Elevated repairs over single pivot
Yeti Change Infinity
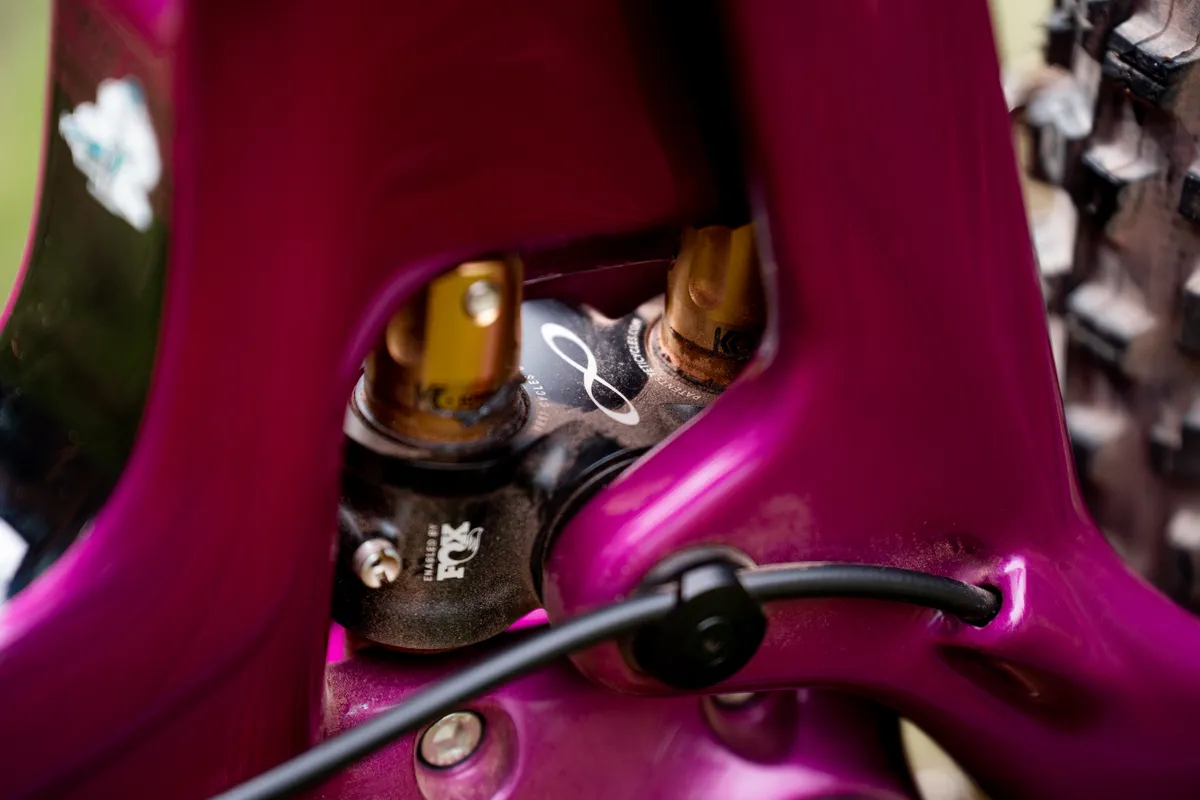

This system makes use of a low pivot, which slides up and down on a pair of vertical shafts, together with an bigger hyperlink that rotates clockwise (if seen from the driveside) on account of the suspension compresses.
The decrease pivot acts much like the rear pivot on the decrease hyperlink of a traditional twin-link design, along with that this pivot strikes vertically in a straight line comparatively than a curving arc centred on the ahead pivot diploma.
Take into accounts you could make the decrease hyperlink of a traditional twin-link bike infinitely extended and horizontal. Then its rear-pivot location would change up and down in a straight, vertical line with no curvature to its path in the slightest degree. That is primarily what Yeti has simulated with its linear sliders (subsequently the title).
What’s the purpose of that? Appropriately, Yeti claims this permits it to get the kinematics to behave one of the best ways it desires correct by way of the journey.
On paper, on the very least, there’s nothing drastically utterly utterly totally different about Yeti’s suspension kinematics in contrast with some frequent twin-link designs.
Though it has managed to extend the anti-squat all through the sag diploma the place it’s wanted most, it then drops off drastically deeper into the journey to minimise pedal kickback, permitting the suspension to work additional freely.
We uncover this trade-off contained in the anti-squat and pedal kickback sections of this textual content material. Nonetheless, it’s not true that the Change Infinity design has a very uncommon or rearward axle path, as some media retailers might need claimed.
Professionals
- Anti-squat peaks throughout the path of sag diploma
- Pedal kickback diminished deeper in journey
Cons
- Elevated repairs over single pivot
Mountain bike suspension phrases outlined
What’s a suspension linkage?

A suspension bar or linkage is a inflexible half all by the suspension system that’s related to its utterly totally different elements with pivots.
To calculate the variety of bars in a suspension design, you’ll have to solely rely these hyperlinks that outline the system’s axle path, anti-squat and anti-rise.
A physique’s entrance triangle have to be used when calculating the variety of bars; the opposite bars are hooked as a lot because it and their motion is printed by it.
Subsequently, single-pivot bikes are two-bar designs. Horst-link or twin-link bikes are four-bar designs, and DW6 (discovered on Atherton Bikes) or Yeti Sixfinity designs (seen on the Yeti 160E) are six-bar layouts.
Bikes that use extra linkages to deal with suspension-leverage costs – resembling faux-bar bikes (single pivots with a linkage) aren’t true four-bar designs.
The Specialised Enduro (a four-bar design with an extra two hyperlinks to stipulate kinematics) isn’t an precise six-bar design regardless of the suspension having six hyperlinks.
What’s the on the spot centre?


On the spot centre (IC) dictates the trail by way of which the rear axle, wheel and every issue hooked as a lot because it, change at a given diploma contained in the journey.
For single-pivot bikes (together with linkage-driven varieties), the IC is just the principle pivot diploma. It doesn’t change; it’s mounted on the mainframe. Subsequently, the rear axle is constrained to maneuver in a seamless arc centred on the pivot.
In a Horst-link or twin-link design, the second centre ‘floats’ on the extent of intersection of hypothetical strains drawn by way of the pivots of the 2 hyperlinks, that are related to the mainframe. On account of the suspension cycles by way of its journey, the second centre strikes.
The state of affairs of the second centre helps outline the degrees of anti-squat, pedal-kickback and anti-rise at a given diploma contained in the journey.
Due to the second centre strikes on account of the suspension cycles by way of its journey, Horst-link, twin-link or six-bar designs afford their designers greater administration over these parameters all by way of the journey.
What’s the centre of curvature?

The centre of curvature (CC) is the surroundings pleasant pivot diploma of a twin-link or Horst-link design.
Take into accounts a drawing compass the place the rear axle acts on account of the pencil and the CC is the sharp diploma caught into the paper – it defines the radius of curvature of the axle path.
For a lot of who draw a line from the axle to the IC, then change the axle a small quantity by way of the journey, then draw that axle-to-IC line as quickly as additional, the purpose at which these strains intersect is the CC.
For single-pivot bikes, the CC is on the important pivot diploma, which can even be the IC. For twin-link or Horst-link bikes, the IC strikes relative to the mainframe. In some circumstances, the CC strikes too. In others, it doesn’t.
For bikes with hyperlinks that counter-rotate (e.g. VPP), the CC strikes considerably. This leads to various curvature of the axle path, and anti-squat values that could possibly be tuned to peak someplace within the midst of the journey vary.
At a given diploma contained in the journey, the CC regularly sits in some unspecified time in the end alongside the swingarm line, connecting the rear axle to the IC.
Subsequently, when calculating anti-squat at a given diploma contained in the journey (see beneath), the IC or the CC could be utilized interchangeably, due to they each agree on the tangential path of the axle.
Nonetheless to see how the anti-squat adjustments all by way of the journey, the place and motion of the CC is useful to check out.
What’s pedal bob?

Relying on the kind of driving the bike is designed for, suspension methods could be designed to supply an organization pedalling platform or prioritise suspension effectivity.
The diploma to which that is prioritised over have an effect on absorption and braking effectivity relies upon upon the supposed use of the bike. A cross-country bike will prioritise a firmer pedalling platform over fine-tuned have an effect on absorption, whereas an enduro bike would put additional emphasis on the latter.
Each time you push down on the pedals, the bike accelerates. This acceleration causes your weight to shift backwards and compresses the rear suspension – an similar to in an accelerating automotive.
This occurs with the rhythmic nature of each pedal stroke, so the bike’s suspension oscillates, or bobs, as you pedal. This oscillation is called pedal-bob.
This motion wastes vitality; the suspension dampers convert this vitality into warmth comparatively than propelling the bike ahead.
On account of the rider areas weight on the pedals, they exert a downward vitality on the underside bracket. This causes the suspension to compress, so the underside bracket strikes downwards on account of the pedals go three and 9 o’clock, after which it rebounds as soon as extra up as they attain six and 12 o’clock.
So in case you moved with the bike and regarded on the cranks from the aspect, the pedals wouldn’t change in a circle, they’d change in an elliptical (oval) path due to the underside bracket strikes up and down on account of the cranks flip.
This implies the rider has to push the pedals additional per revolution than they might if there was no pedal bob, nevertheless the rear wheel nonetheless turns the an similar quantity. This additional distance is proportional to the wasted vitality.
Anti-squat

Similtaneously pedal-bob, pedalling forces pull on the chain. This, in flip, influences the rear suspension, extending it and lifting the rider.
Anti-squat is a measure of how tons the suspension resists pedal bob. On account of the squat vitality (as a consequence of acceleration) compresses the rear suspension beneath energy, the anti-squat vitality counteracts this.
This vitality comes from two sources: the driving vitality from the rear wheel and the chain-pull vitality.
The driving vitality is talked about little, nonetheless it’s simple sufficient to know.
For any bike, take into consideration the surroundings pleasant swingarm as a straight line connecting the rear axle to the second centre. That’s known as the swingarm line. By definition, this line might go by way of the centre of curvature, nonetheless for simplicity, we’ll merely talk about with the IC correct proper right here.
The driving vitality pushes by way of the swingarm line. The power consists of the traction vitality propelling the bike ahead, plus the compressive vitality generated by the chain stress.
If the second centre is greater than the rear axle – so the swingarm line is angled upwards – an element of this driving vitality acts to push the mainframe upwards when pedalling, counteracting its tendency to squat down beneath acceleration.
The chain-pull vitality comes from the stress contained in the chain, which regularly furthermore pulls the rear wheel downwards relative to the mainframe, and so acts to carry the mainframe up, countering its tendency to squat beneath pedalling load.
Considering of it one totally different method, (for lots of bikes) the cassette strikes up and away from the chainring on account of the suspension compresses, on account of this actuality the stress contained in the chain resists this movement by pulling the swingarm down.
The quantity of anti-squat vitality relies upon upon the angle of the swingarm line, whereas the quantity of chain-pull anti-squat relies upon upon the angle of the chainline relative to the swingarm line.
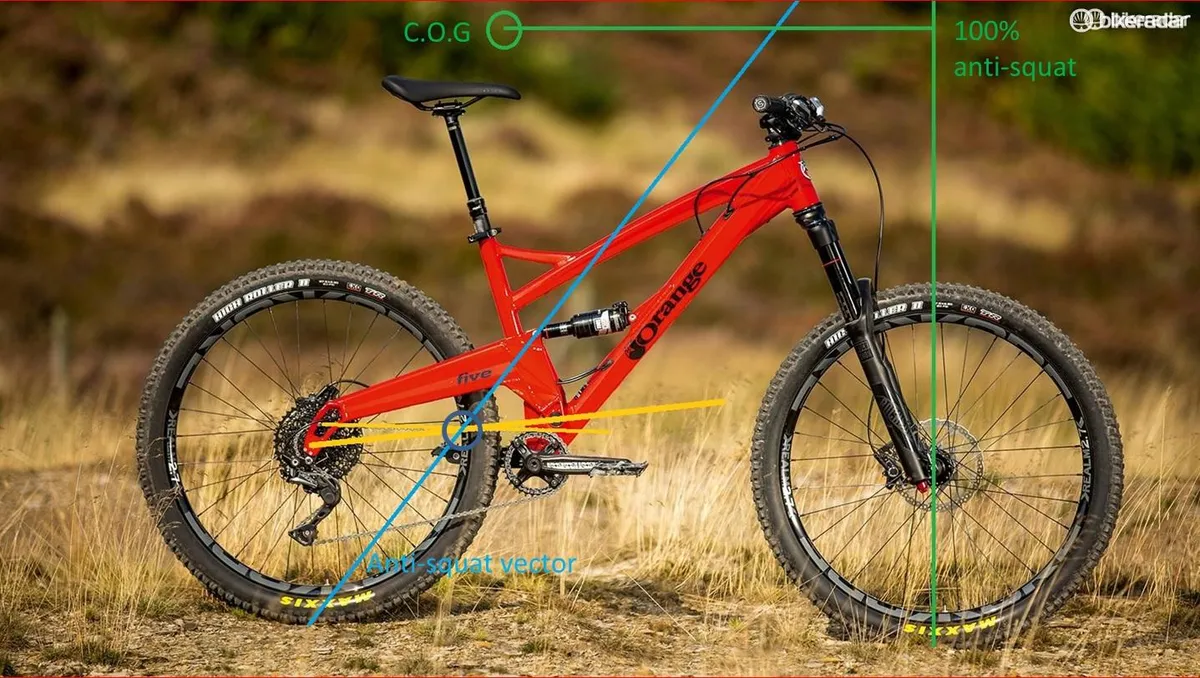

The final quantity of anti-squat could be labored out by the intersection of the swingarm line and the higher chainline.
The purpose the place they intersect is the important issue. A 3rd line can then be drawn from the rear contact patch by way of this diploma of intersection. That’s known as the anti-squat vector, and its gradient defines the quantity of anti-squat.
Evaluating this line to the centre of gravity and the doorway contact patch tells you strategies the anti-squat vitality compares to the squat vitality as a consequence of acceleration. In simplistic phrases, 100 per cent anti-squat would level out that the squat and anti-squat forces cancel out precisely. In principle, this leads to zero pedal bob.
If the anti-squat vector is greater than the centre of gravity when it’s straight above the doorway contact patch, you will have gotten bigger than 100 per cent anti-squat. If it’s beneath the COG when it’s above the doorway axle, you will have gotten lower than 100 per cent anti-squat.
Importantly, the anti-squat share is unbiased of how exhausting you pedal. For a lot of who pedalled twice as exhausting, you’d velocity up twice as quick, and so the squat vitality would double. On the an similar time, the anti-squat vitality would double due to there could be double the stress contained in the chain. So the anti-squat share would maintain the an similar.

So why aren’t all bikes designed to have 100 per cent anti-squat? Wouldn’t that point out an finish to pedal bob? Appropriately, as you would possibly want guessed by now, it’s not that simple.
For starters, there is not a such issue as a solution to precisely estimate the place of the rider’s centre of gravity (it varies relying on the rider and one of the best ways they change about when driving).
Even in case you would possibly estimate the rider’s centre of gravity, the place of the bike’s entrance centre impacts the share of anti-squat. That adjustments with the physique measurement, so that you just’d ought to account for that too. Most bike designers don’t.
For lots of bikes, the quantity of anti-squat furthermore relies upon upon what gear you’re in.
The exception to that is the case of a bike the place the CC is strictly in line with the perfect of the chainring. In one other case, the gathering of rear sprocket will give utterly utterly totally different parts of anti-squat, due to the intersection of the chainline and the swingarm line will change.

Fully utterly totally different chainrings upset factors too, with smaller chainrings leading to larger anti-squat. That is an argument in favour of quite a few chainrings, due to larger anti-squat is usually useful when climbing.
One totally different complication is that, for lots of bikes, the degrees of anti-squat fluctuate on account of the bike strikes by way of its journey – normally by tons of – so how tons dynamic sag you run will impression anti-squat and on account of this actuality pedalling effectivity.
So altering spring pressures, or driving up utterly utterly totally different gradients, will end in utterly utterly totally different anti-squat percentages.
Let’s take into accounts for a minute that you just might design for one physique measurement, one gear, one diploma contained in the journey, and for a rider whose centre of gravity was mounted.
In that case, you could design a bike to withstand squat precisely, if the flexibility was utilized merely via a motor. That’s why it’s doable, though not principally advantageous, to design a bike that resists acceleration-induced squat virtually completely.
Nonetheless mountain bikes aren’t motorbikes. When pedalling, a rider’s weight strikes up and down barely as their legs flip. This introduces one totally different oscillation-driving vitality, which causes the bike to bob bigger than the acceleration vitality alone, considerably when pedalling standing up.
Because of this, many bikes have bigger than 100 per cent anti-squat to assist counter the blended squat forces from acceleration and the rider’s weight motion.
Due to downhill bikes are designed to be pedalled standing up solely, they normally have anti-squat ranges far larger than 100 per cent.
In principle, in case you would possibly pedal completely merely with out jerking up and down, bikes with bigger than 100 per cent anti-squat would rise upwards, like an inchworm, comparatively than squat down when pedalling. This has led some suspension analysts to say that 100 per cent anti-squat is the right quantity for the simplest effectivity.
Nonetheless the jerky physique weight actions of the rider point out bikes want a bit additional anti-squat to beat this. Due to this vitality adjustments relying on the rider’s pedalling vogue, and isn’t principally partly with the acceleration squat vitality, there’s no decision to say what the only anti-squat worth is.
So don’t be fooled by any marketeer claiming their bike has “optimised pedalling effectivity”. It’s pretty additional refined than that.
Pedal kickback
There could be a draw once more to excessive ranges of anti-squat. The anti-squat vitality will depend upon the cassette shifting away from the chainring on account of the suspension compresses. That’s known as chain progress.
More often than not, the cassette rotates ahead to permit the chain sufficient slack for the suspension to compress.

Nonetheless, if the cassette can’t spin ahead due to the rear wheel is locked up (beneath heavy braking, for instance), the crank could also be compelled to rotate backwards.
The motion of the crank contained in the case of a non-rotating cassette is called pedal kickback, which may set off a really harsh journey really actually really feel.
The extra chain-pull anti-squat a bike has, the extra pedal kickback it generates. These phrases can roughly be considered two names for a similar situation.
For single-pivot bikes with an on the spot centre that’s larger than prime of the chainring (for instance, high-pivot bikes with out an loafer pulley), the quantity of pedal kickback is proportional to the anti-squat.

For bikes with excessive pedal-kickback values, its have an effect on can usually flip into noticeable – considerably on highly effective tracks with a great deal of sudden impacts or when hitting bumps with the rear wheel locked up.
It will even be felt when climbing. On account of the chain is regularly beneath stress when pedalling, the anti-squat by definition, resists the suspension’s motion. So bikes with excessive anti-squat could be harsh and unreactive when pedalling over bumps.
In loads of driving conditions, pedal kickback in itself is just not one issue you’re additional extra more likely to uncover.

Nonetheless the extra chain progress/pedal kickback you will have gotten, the extra the chain, cassette and derailleur cage must maneuver to have the flexibility to permit the suspension sufficient slack contained in the chain to react. This may occasionally have a detrimental have an effect on on suspension sensitivity, considerably when utilizing a clutch derailleur.
So there’s a stability to be struck correct proper right here: additional anti-squat usually means greater pedal-efficiency, nonetheless tends to point worse sensitivity.
That is the place Horst-link and twin-link designs have a possible revenue over single-pivot methods.
All such designs attribute on the spot centres that migrate on account of the suspension strikes by way of its journey.
Some, notably these with counter-rotating hyperlinks, could be designed such that the centre of curvature migrates considerably as correctly. In that case, the angle of the swingarm line varies with journey in a method that isn’t doable with a single-pivot design.
This makes it doable to have excessive ranges of anti-squat close to the sag diploma (the place it’s wanted to withstand bob), whereas having lots a lot much less anti-squat, and on account of this actuality lots a lot much less pedal kickback, elsewhere contained in the journey.
That is actually not true of all multi-link bikes, nonetheless these with counter-rotating hyperlinks boast anti-squat values that peak between 20 and 45 per cent journey the place it’s wanted most.
This bell-shaped anti-squat profile is typical of dual or Horst-link designs with counter-rotating hyperlinks. The result’s good pedalling effectivity all by way of the pedalling zone, with minimal additional pedal kickback additional into the journey.
There are furthermore similarities contained in the anti-squat profile between some single-pivot and twin-link bikes.
In circumstances the place the hyperlinks co-rotate, the centre of curvature doesn’t change considerably relative to the mainframe all by way of the journey. This implies the rear axle strikes in an arc with a seamless radius relating to the CC, much like a single-pivot, leading to related anti-squat behaviour. Notably, the anti-squat normally drops off all by way of the stroke.
The steeper the anti-squat drops off, the lots a lot much less pedal kickback there could also be throughout the path of the very best of the stroke, nonetheless the extra the pedalling effectivity could also be affected by dynamic sag.
Nonetheless, the centre of curvature could be designed to sit down down ready which can be impractical to position a bodily pivot (resembling all by the radius of the wheel, or within the midst of the doorway triangle).
On this sense, the designers can produce kinematic behaviour which can be highly effective, in observe, to duplicate with a single pivot.
With out redesigning your bike, you’ll be able to tune the quantity of anti-squat it has by swapping chainrings. Larger rings will end in diminished anti-squat nonetheless lots a lot much less pedal kickback, or vice versa.
Further merely, driving over highly effective terrain contained in the smaller cassette cogs (and larger chainrings whenever you’ve quite a few) will end in lots a lot much less pedal kickback. So shift into the tougher gears ahead of dropping correct into a tough descent for max sensitivity and minimal methods.
Excessive-pivot bikes bypass this. The loafer means they exhibit virtually zero upper-chain progress or pedal kickback. Nonetheless, because of the excessive IC, they nonetheless have important ranges of anti-squat due to the driving vitality alone.
What’s anti-rise (or brake jack)?
One totally different idea that impacts suspension effectivity is anti-rise, generally generally known as brake jack. That is primarily the have an effect on of the rear brake vitality on the suspension. It really works a bit like anti-squat nonetheless in reverse.
Beneath braking, the rider’s weight shifts ahead as a consequence of deceleration, which causes the rear suspension to rise or lengthen. Nonetheless, the power going by way of the rear brake caliper acts to compress the suspension, pushing the mainframe down. This resists the bike’s pure tendency to wish to elevate on the rear, so it stays additional stage beneath braking.
For a lot of who compress the rear suspension whereas the rear wheel stays nonetheless, the caliper will change spherical relative to the disc. For a lot of who pull the rear brake when driving forwards, the braking torque from the caliper acts to compress the suspension by an quantity proportional to this motion, relative to the disc.
The quantity of anti-rise relies upon upon the extent to which the caliper should maneuver all through the disc and that’s dependent upon the place of the second centre.
Take into accounts a line between the rear contact patch and the IC: the shallower the gradient of that line, the decrease the quantity of anti-rise. That is generally known as the anti-rise vector and could be utilized to calculate the share anti-rise throughout the an similar method on account of the anti-squat vector contained in the diagram above.
Correct proper right here, bigger than 100 per cent anti-rise implies that pulling the rear brake solely would set off the rear suspension to compress, whereas lower than 100 per cent anti-rise implies it may well lengthen.
Horst-link or twin-link bikes with roughly parallel hyperlinks have an on the spot centre that’s very far ahead.
Subsequently, the anti-rise vector sits at a shallow angle, leading to low ranges of anti-rise. Bikes with on the spot centres positioned excessive up and rearward have additional anti-rise.
Trek’s ABP design sees the brake caliper hooked as a lot because the seatstay, comparatively than the chainstay. The seatstay strikes on an arc that is outlined by a floating on the spot centre, like a Horst-link, which is additional ahead of the principle pivot, so anti-rise is diminished relative to a chainstay-mounted caliper.

Brake arms have been used to related have an effect on – they scale back anti-rise by limiting the brake’s have an effect on on the suspension.
Excessive ranges of anti-rise are sometimes thought to make the suspension really actually really feel firmer and fewer reactive over bumps, leading to a harsh feeling when braking. The importance of this have an effect on is debatable.
Nonetheless, anti-rise furthermore helps the rear suspension sit deeper into its journey, so it’s disputable whether or not or not or not excessive anti-rise values end in roughly traction beneath braking.
An similar to anti-squat, the quantity of anti-rise is a trade-off between preserving the bike’s geometry and the suspension sensitivity. No bike is totally unbiased of braking forces and it’s debatable whether or not or not or not these braking forces are principally a nasty situation.
Axle path outlined
The axle path is particularly the road the rear axle takes on account of the suspension strikes, measured relative to the mainframe. The path of the axle path at any diploma contained in the journey is at appropriate angles to the swingarm line, which connects the axle to the second centre, via the centre of curvature.
Subsequently, you’ll be able to take into consideration anti-squat purely in relation to axle path – the extra the axle path strikes away from the underside bracket, the extra anti-squat. That could be very tons the an similar as saying a better on the spot centre leads to additional anti-squat, as described above.
An extra rearward axle path may additionally assist a bike to soak up sure bump forces for causes unrelated to the chain. Nonetheless for lots of bikes, the axle path solely strikes rearwards by just a few millimetres at most.
As rapidly as as quickly as additional, high-pivot bikes are a notable exception. Their axle path strikes considerably rearwards all by way of the journey.
It makes intuitive sense {{{that a}}} rearward path permits the wheel to maneuver out of one of the best ways whereby additional merely when confronted with large bumps. The power produced by these is rearward together with upward (the power vector elements inside the trail at appropriate angles to the purpose on the wheel the place it contacts the bump).
Subsequently, it stands to set off {{{that a}}} additional rearward axle path could also be bigger in a position to take in these large bumps, due to the axle strikes in a path that’s bigger aligned with the bump vitality.
For an analogy, it’s helpful to ponder suspension forks with utterly utterly totally different head angles. The top angle defines the axle path of the doorway wheel. Slacker head angles, and on account of this actuality forks, have a tendency to soak up kerb-sized bumps additional merely nonetheless are additional weak to flex and binding when pushing vertically downwards contained in the automotive park or when touchdown to flat.
The an similar situation is occurring with a high-pivot bike – large bumps push the axle inside the trail it should go. The flex and binding subject doesn’t apply to the rear suspension due to they use a linkage comparatively than telescoping by way of bushings.
Take into consideration it one totally different method. A rearwards axle path means the rear wheel travels backwards relative to the mainframe on account of the suspension compresses. This implies the wheel strikes additional slowly relative to the bump and so strikes up and over it additional slowly too.
Having stated that, one take a look at demonstrated a full suspension bike required 30–60 per cent lots a lot much less energy than a hardtail to journey over simulated highly effective terrain in a lab.
So, if high-pivot suspension absorbs bumps additional effectively, it stands to set off that these bumps will rob the bike of lots a lot much less ahead momentum, nonetheless that is largely unproven.
Every method, for bikes with out an loafer pulley, that is all pretty tutorial. In that case, the potential bump-absorption benefit of a (barely) additional rearward axle path is negated by the rise in chain progress and anti-rise they produce.
Leverage curves vs spring curves
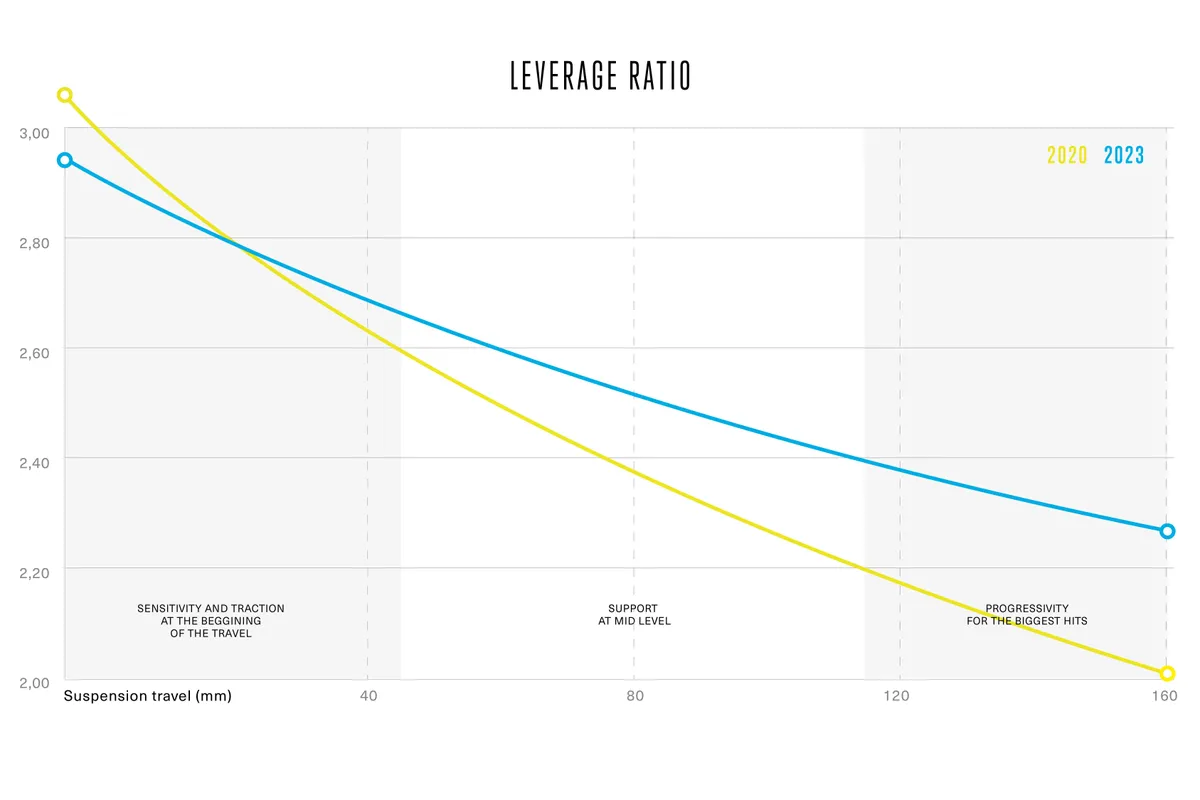
Arguably an important aspect of suspension kinematics, in relation to journey really actually really feel, is the leverage curve – one of the best ways whereby the leverage ratio adjustments by way of the journey.
The leverage ratio is the ratio between the outlet the rear wheel strikes and the outlet the shock strikes on account of the suspension cycles.
The frequent leverage ratio is due to this actuality the ratio of rear-wheel journey to the stroke of the shock. Bikes with larger frequent leverage ratios (non permanent stroke shocks for the journey) might need a bonus in relation to sensitivity due to there’s additional leverage to beat the friction contained in the shock.
Nonetheless, excessive leverage ratios demand larger spring pressures and better forces contained in the damper. There’s furthermore usually lots a lot much less oil contained throughout the damper to cope with warmth on extended runs. Consequently, bikes with decrease frequent leverage ratios (longer stroke shocks for a given journey) are normally additional dependable and extra fastened.
Important aspect of the leverage curve is just not the frequent ratio nonetheless how the leverage ratio adjustments all by way of the journey. The upper the ratio, the better it’s to compress the shock, so bikes that begin with a excessive leverage ratio and finish with a decrease one end in a progressive suspension motion, which suggests it’s tougher to entry the final phrase a part of the bike’s journey.
It’s counter-intuitive, nonetheless for a bike to be progressive the leverage graph slopes downwards as you endure the journey.
By evaluating the leverage ratio at sag with the leverage ratio at bottom-out, the physique progressivity could be calculated as a share.

Whether or not or not or not you will have gotten a coil shock or air shock might affect leverage and spring curves.
With a coil shock (which has a seamless spring worth), the quantity of progressivity is printed by the leverage curve alone. With an air shock, the end-stroke progressivity could be fine-tuned (to some extent) with quantity spacers. Lowering the spring quantity with quantity spacers creates additional progress.
The ultimate firmness of the suspension on the wheel is called the wheel worth. This typically is a operate of the shock’s spring worth and the leverage curve – each of which can fluctuate all by way of the journey. A leverage ratio that decreases throughout the path of the very best of the stroke has the similar have an effect on on the wheel worth as a spring worth which will enhance throughout the path of the very best of its stroke. Each end in a progressive suspension motion.
A linear leverage ratio with a progressive shock would possibly present the similar wheel worth (full progressivity) to a progressive leverage ratio with a linear shock. Nonetheless these two setups will nonetheless current utterly utterly totally different traits.
For starters, turning into a really progressive air shock (full of quantity spacers) to a bike with a linear or regressive leverage curve will end in a quicker end-stroke rebound because of the excessive spring vitality deep contained in the journey.
A progressive leverage curve furthermore generates additional resistance from the damper throughout the path of the very best of the stroke, so each spring and damping forces are used to withstand bottom-out. Whereas, contained in the case of a linear leverage curve, solely the spring vitality ramps up throughout the path of the very best of the stroke.
The share progressivity doesn’t inform the entire story – what factors most is the place contained in the journey the physique is progressive. In a number of phrases, the kind of the leverage curve.
For instance, bikes with a ‘hanging’ leverage curve have a excessive leverage ratio firstly of the journey to melt the preliminary stroke and drop shortly to a decrease ratio within the midst of the stroke so as in order so as to add assist after sag. That is notably related when utilizing an air shock due to they’re normally firmer at first stroke and softer contained in the mid-stroke, relative to a coil.
The selection case is a type of humped kind, the place the utmost leverage happens within the midst of the stroke. As you would possibly anticipate, this leads to a firmer starting stroke and a softer mid-stroke than the “hanging” curve.
Blended with an air shock, this lack of mid-stroke assist may end up in a wallowing really actually really feel in compressions, together with elevated pedal-bob – it’s not solely anti-squat that impacts pedal effectivity.
The leverage curve must be progressive throughout the path of the very best of the stroke, nonetheless this isn’t the place the assistance is required with an air shock. Bikes with this sort of leverage curve would possibly match bigger with a coil spring. Bikes that lack assist contained in the mid-stroke usually tend to require larger ranges of compression damping to withstand mid-stroke wallowing, nonetheless this negatively impacts sensitivity all by way of the stroke.
How progressive your bike need to be is completely private – it is dependent upon the rider’s energy, terrain and driving vogue.
Because of trendy air shocks, progressivity is certainly tunable by the very best particular person, nonetheless a bike’s leverage curve nonetheless performs a vast function in one of the best ways it feels, notably contained in the mid-stroke, and that’s one issue that may’t regularly be remedied with shock setup.
Ought to I select a bike primarily based completely on its suspension design?

Whereas suspension design is crucial to ponder when selecting a mountain bike, it should not be the deciding topic.
It’s best to first have an thought-about how tons suspension journey you want for the paths you could be driving, together with an thought-about the sizing and geometry required.
Whether or not or not or not single-pivot, Horst or twin-link, it’s the small print of pivot placement that make the whole distinction.
Bikes with the an similar fundamental building normally current very utterly utterly totally different kinematics and journey really actually really feel, on account of this actuality it is going to possible be silly to say one design performs bigger than one different.
Single-pivot suspension affords simple reliability nonetheless affords designers little administration over the bike’s kinematics.
Along with linkages makes it doable to manage the physique’s leverage curve and progressivity, whereas Horst or twin-link layouts can enhance administration over the pedalling and braking behaviour too, considerably if the hyperlinks counter-rotate.
Nonetheless is {{that a}} bonus? It relies upon upon completely on what the designers do with that administration due to it’s not regularly for the only.
Whereas the rear shock setup stays an important aspect of rear suspension effectivity, an superior shock tune obtained’t make up for a flawed suspension design.
That is notably true if a physique has extreme chain progress or a leverage curve that’s not supportive sufficient for the rider’s wants. In that case, the shock setup could also be at greatest a sticking plaster for poor design.
In the end, the suspension traits that work greatest for you could depend upon one of the best ways you journey. For instance, one criticism levelled at true single-pivot bikes is that they are usually fairly linear, nonetheless which may go correctly with some riders preferring an opulent really actually really feel.
Equally, those that wish to hammer down highly effective terrain could not like a bike with an excessive amount of pedal-kickback, whereas some would possibly much like the pedal-efficient and interactive really actually really feel that comes with excessive ranges of anti-squat.
It’s largely a matter of favor and that the majority positively explains why we nonetheless see such an infinite array of designs throughout the market.
